The process of wire drawing
Time:
2024-05-20
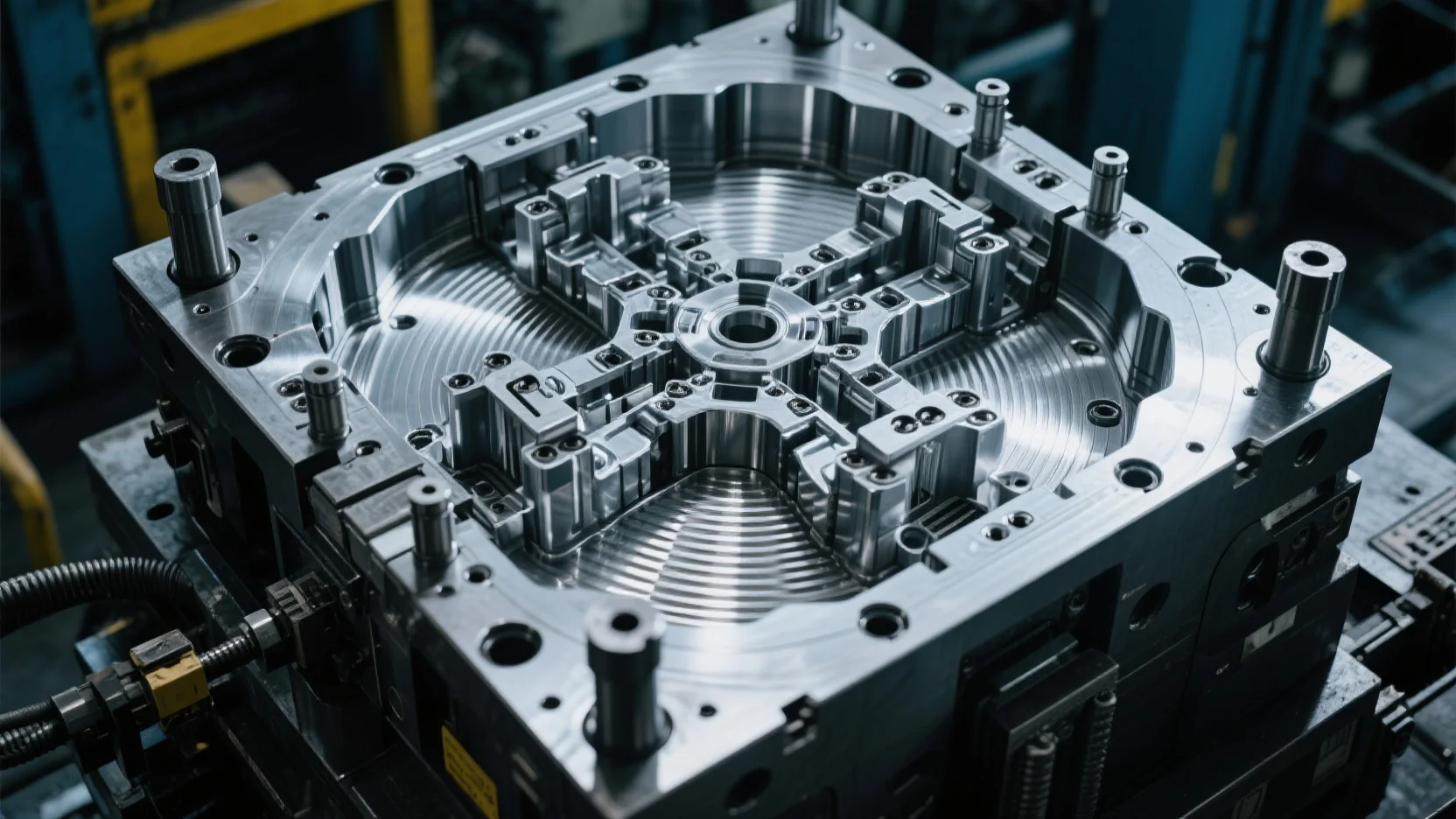
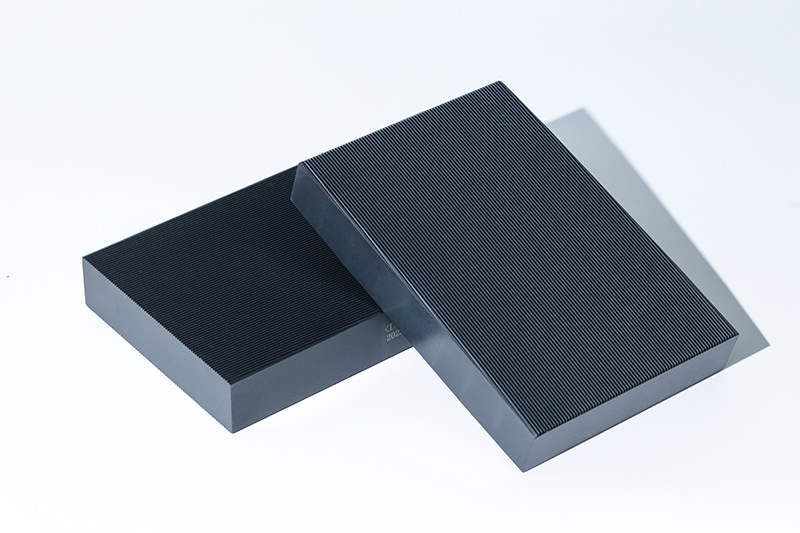
Thread rolling plates - two square templates used on a thread rolling machine, divided into two parts, one long and one short, with thread patterns on them, used as a mold to press and form screw blanks into threads. Thread rolling plates are special tools used for processing taps and bolts.
Thread rolling plates are the most commonly used threading tools in the standard fastener industry for processing screws and bolts. The processing principle mainly uses cold extrusion, which has the advantages of high production efficiency, low processing cost, high precision and strength of the processed threads, and good surface quality, and has been widely used.
Thread Rolling Plate Processing Technology
The manufacturing process of thread rolling plates is: blanking - forging - spheroidizing annealing - machining - cold rolling thread - quenching + low temperature tempering - grinding
Forging:
This process involves repeatedly upsetting and drawing the bar material to ensure uniform carbide distribution and alter the internal flow line distribution of the steel.
The desired flow line distribution of the thread rolling plate is shown in the figure.
Spheroidizing Annealing:
The blank has high hardness and uneven composition. To reduce hardness and facilitate machining, and to prepare the microstructure for the final heat treatment. Technical indicators are:
① 9SiCr steel, hardness 197~241HB
② Decarburization layer depth shall not exceed 1/2 of the machining allowance. Heat to 790℃ for 2h, furnace cool to 710℃, then hold for 7h, then furnace cool to 500℃, air cool. Microstructure after spheroidizing annealing: spheroidized pearlite.
Cold Rolling Thread:
This is a key process in the manufacturing process, using rolling pins to process the threads. The precision directly affects the quality of the processed external threads, so the technical requirements should be strictly followed.
Heat Treatment of Thread Rolling Plates:
① Technical requirements: Hardness 58~62HRC; Quenched martensite less than grade 2.5 [in metallographic inspection (500x)]; Tooth surface without oxidation, decarburization or pitting.
② Process flow: preheating - heating - cooling - cleaning - tempering - hardness inspection - blackening - appearance inspection.
Tempering Process:
① Due to the effect of Si and Cr elements, the tempering stability of the steel is improved, so tempering is carried out at 200~230 °C. At this temperature, the hardness decreases very little, and the hardness is still very high after tempering.
② The microstructure after tempering is: M return + granular carbides + a small amount of residual austenite.
Previous Page
Next Page

027-59370266
027-59370566
market@efeng.com
No. 6, Chuangye Avenue, Ezhou Economic Development Zone, Ezhou City, Hubei Province
Copyright © 2025 Emei Special Equipment (Wuhan) Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.